SAP PM | SAP PM Full Form | SAP Plant Maintenance Job | SAP Full Form | SAP PM Jobs | PM Module in SAP | SAP Plant Maintenance | SAP PM Interview Questions
SAP PM Full Form is SAP Plant Maintenance. It is a module within the SAP ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system that is designed to help organizations manage their maintenance processes more efficiently. SAP Full Form is "Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing."
SAP PM Full Form | SAP Plant Maintenance Job | SAP Full Form | SAP PM Jobs | PM Module in SAP | SAP Plant Maintenance | SAP PM Interview Questions
- SAP PM is a software module designed for managing and maintaining equipment and assets in industrial settings.
- Key features of SAP PM include asset management, maintenance planning, and work order management.
- SAP PM helps organizations optimize maintenance schedules, reduce downtime, and increase equipment reliability.
- To implement SAP PM, organizations need to have a robust IT infrastructure and a skilled team of professionals who can configure and customize the software to meet their specific needs.
- SAP PM integrates with other SAP modules, such as SAP MM (Materials Management) and SAP FI (Financial Accounting), to provide a comprehensive solution for managing assets and resources.
- SAP PM is used by a wide range of industries, including manufacturing, energy, utilities, and transportation.
- To get the most out of SAP PM, organizations should consider investing in training and education for their staff, as well as engaging with a trusted SAP consulting partner.
- By implementing SAP PM, organizations can improve their maintenance operations, reduce costs, and increase the overall efficiency and productivity of their assets and equipment.
The SAP PM module allows users to plan, schedule, and execute maintenance tasks for equipment, machines, and other assets. It also provides tools for tracking maintenance costs, managing work orders, and analyzing maintenance data to identify areas for improvement.A
SAP PM Jobs or SAP Plant Maintenance Job involves working with the SAP Plant Maintenance (PM) module of the SAP software system to manage the maintenance of plants, equipment, and assets in an organization. The job typically includes the following responsibilities:
- Developing and implementing SAP PM strategies and maintenance plans to ensure the efficient operation of equipment and facilities.
- Overseeing the maintenance of plant equipment and assets, including scheduling and tracking maintenance activities, creating and updating work orders, and managing maintenance resources.
- Collaborating with other departments to identify and resolve maintenance issues and ensure the smooth operation of production processes.
- Analyzing data from the SAP PM module to identify trends, develop maintenance reports, and make data-driven decisions.
- Participating in the development and implementation of new systems, processes, and procedures to improve the effectiveness and efficiency of the maintenance function.
- Managing and training staff on the SAP PM module and related maintenance processes and procedures.
To qualify for a SAP Plant Maintenance job, candidates typically need a degree in engineering, computer science, or a related field, as well as experience working with the SAP PM module and knowledge of maintenance management principles and practices. Strong analytical, problem-solving, and communication skills are also essential.
SAP PM Interview Questions
Following article describes the complete overview of SAP PM which is useful to prepare for SAP PM Interview Questions, by reading the complete article you will get complete insight of SAP PM
SAP Plant Maintenance (SAP PM) is a software module developed by SAP SE that is used for managing maintenance activities in industrial plants, such as manufacturing facilities, power plants, and chemical plants. SAP PM is a part of the larger SAP Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system, which integrates all of the key business processes of an organization into a single, unified system.
SAP PM is designed to streamline the maintenance processes of a plant, from planning and scheduling of maintenance activities to execution and reporting of work orders. It provides tools for managing equipment maintenance schedules, tracking maintenance costs and downtime, and managing work orders and maintenance personnel. SAP PM also includes features for managing spare parts inventory, monitoring equipment performance, and tracking regulatory compliance.
One of the key benefits of SAP PM is its ability to provide real-time data on maintenance activities, which enables plant managers to make informed decisions about equipment maintenance and repair. It also helps to reduce maintenance costs and improve the overall reliability of plant equipment by providing insights into equipment performance and identifying potential issues before they become major problems.
SAP PM can be customized to meet the specific needs of an organization, and can be integrated with other SAP modules such as SAP Materials Management (MM) and SAP Sales and Distribution (SD). It is widely used in a variety of industries, including manufacturing, energy and utilities, and transportation
PM Module in SAP | SAP Plant Maintenance Types
1. Equipment management:
This includes managing the maintenance of all equipment in the plant, including planning and scheduling maintenance tasks, tracking equipment performance, and monitoring spare parts inventory.
2. Preventive maintenance:
This involves creating and scheduling maintenance plans for equipment based on manufacturer recommendations, historical data, and other factors to prevent breakdowns and extend the lifespan of equipment.
3. Corrective maintenance:
This involves managing repairs for equipment that has broken down or failed, including creating and assigning work orders, tracking repair costs, and managing maintenance personnel.
4. Work order management:
This includes managing the creation, assignment, and execution of work orders, as well as tracking their progress and completion.
5. Maintenance planning and scheduling:
This involves developing and managing maintenance plans and schedules for equipment maintenance tasks, as well as ensuring that maintenance tasks are scheduled and completed in a timely manner.
6. Resource management:
This includes managing maintenance personnel and resources, such as spare parts inventory and tools, to ensure that maintenance tasks can be completed efficiently and effectively.
7. Reporting and analytics:
SAP PM provides a range of reporting and analytics tools to help plant managers and maintenance personnel monitor equipment performance, track maintenance costs and downtime, and identify areas for improvement.
8. Integration with other SAP modules:
SAP PM can be integrated with other SAP modules such as Materials Management (MM), Sales and Distribution (SD), and Financial Accounting (FI) to streamline business processes and improve overall efficiency.
9. Regulatory compliance:
SAP PM provides features for tracking and ensuring compliance with regulations and standards related to equipment maintenance and safety.
10. Mobile maintenance:
SAP PM also provides mobile capabilities, allowing maintenance personnel to access work orders and maintenance data from mobile devices in the field
Example of how SAP PM might be used in a manufacturing plant:
Let's say there is a manufacturing plant that produces automotive parts. The plant uses a range of equipment, including presses, stamping machines, and conveyor belts, to produce these parts. To ensure that the equipment is maintained properly and to avoid any unplanned downtime, the plant decides to implement SAP PM.
First, the plant sets up the equipment in the SAP PM system, including all relevant data such as equipment types, manufacturers, and maintenance plans. They also create a master data for each equipment, including serial numbers, part numbers, and detailed descriptions.
Next, the plant develops preventive maintenance plans for each piece of equipment based on manufacturer recommendations and historical data. The maintenance plans include details such as the frequency of maintenance tasks, the estimated duration of each task, and the materials and spare parts required.
Once the preventive maintenance plans are established, the plant schedules the maintenance tasks using the SAP PM system. They can use the system to create work orders, assign tasks to maintenance personnel, and track the progress of each task.
In addition, the plant can use SAP PM to manage corrective maintenance tasks. When equipment breaks down or malfunctions, they can create work orders to address the issue, assign tasks to maintenance personnel, and track the progress of each task.
SAP PM also provides the plant with real-time data on equipment performance and maintenance costs, allowing them to make informed decisions about equipment maintenance and repair. The reporting and analytics tools in SAP PM can also help identify areas for improvement and optimize maintenance processes.
In conclusion, SAP PM helps the plant streamline their maintenance processes, improve equipment reliability, and reduce downtime and maintenance costs.
In SAP Plant Maintenance (PM), a notification is a record that informs the maintenance department of a problem or an issue related to an equipment or a technical object. Notifications can be used to report malfunctions, damages, or defects, or to request preventive maintenance work.
Notifications
in SAP PM can be created by anyone with access to the system, such as equipment operators or maintenance personnel. When a notification is created, it is assigned a priority level and is routed to the appropriate person or team for further action.
Notifications in SAP PM can contain a variety of information, including the equipment or technical object affected, a description of the problem, and the location of the equipment. They can also include details such as the estimated time required to resolve the issue, the materials and spare parts required, and any safety or regulatory requirements that must be considered.
Once a notification is created, it can be processed in several ways. For example, it can be converted into a maintenance order, which is used to schedule and execute maintenance work. It can also be used to request a quotation for external services or to create a purchase requisition for materials and spare parts required to resolve the issue.
Notifications in SAP PM are a critical component of the maintenance process, as they enable organizations to quickly identify and address equipment issues, reduce downtime and repair costs, and ensure compliance with safety and regulatory requirements. They also provide a central repository of information that can be used to track equipment performance, identify recurring issues, and improve maintenance processes over time.
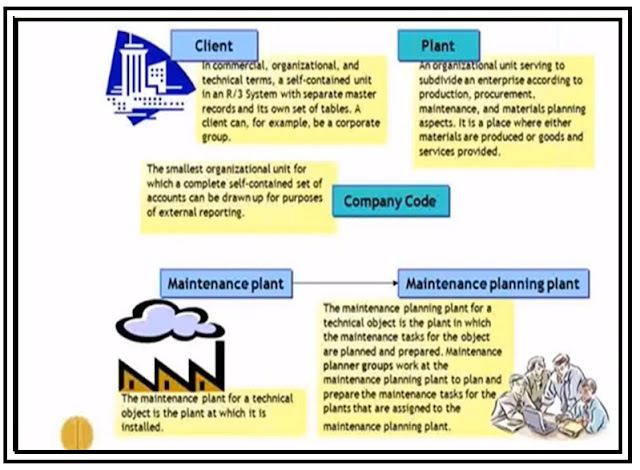
In SAP Plant Maintenance (PM), a functional location is a technical object that represents a specific location in a plant or facility where maintenance activities are performed. A functional location can be a physical asset, such as a machine or a piece of equipment, or a non-physical asset, such as a building or a room.
Functional locations
in SAP PM are used to organize and manage maintenance activities. They provide a hierarchical structure that allows maintenance personnel to easily locate and access equipment, and to track maintenance activities at each location.
To create a functional location in SAP PM, you must first define the structure of the location hierarchy, including the levels of the hierarchy, the names of the functional locations, and the relationships between them. Once the hierarchy is defined, you can create functional locations and assign them to the appropriate levels in the hierarchy.
Each functional location in SAP PM contains a range of information, including a description of the location, its location in the hierarchy, the equipment and assemblies associated with the location, and the maintenance plans and work orders associated with the location.
Functional locations in SAP PM are an important component of the maintenance process, as they provide a centralized repository of information about equipment and locations, and enable maintenance personnel to easily locate and access equipment for maintenance activities. They also facilitate the tracking of maintenance activities at each location, which can help organizations identify trends and optimize maintenance processes over time.
maintenance work is performed. Work centers can be physical locations, such as a maintenance shop or a production line, or they can be virtual groups, such as a team responsible for performing maintenance work on a specific type of equipment.
Work Centers
in SAP PM are used to organize and manage maintenance activities. They provide a centralized location for maintenance personnel to perform work, and enable organizations to track and manage maintenance work orders and schedules.
To create a work center in SAP PM, you must first define the basic details of the work center, such as its name, description, and location. You can also assign resources to the work center, such as personnel, tools, and equipment. Once the work center is defined, you can create maintenance work orders and assign them to the appropriate work center.
Each work center in SAP PM contains a range of information, including the resources assigned to the work center, the maintenance plans and work orders associated with the work center, and the availability of resources for performing maintenance work.
Work centers in SAP PM are an important component of the maintenance process, as they provide a centralized location for maintenance work and enable organizations to track and manage maintenance activities more effectively. They also facilitate the allocation of resources for maintenance work, which can help organizations optimize their maintenance processes over time.
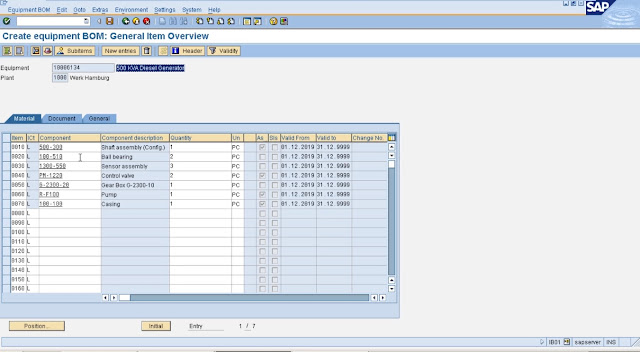
In SAP Plant Maintenance (PM), a Bill of Materials (BOM) is a list of all the components and materials required to maintain or repair a piece of equipment. The BOM provides a detailed breakdown of all the parts required for maintenance activities, including their part numbers, quantities, and descriptions.
Bill of Material (BOM)
In SAP PM are used to streamline the maintenance process by ensuring that all the required parts and materials are available before maintenance activities begin. This helps to reduce downtime and improve maintenance efficiency, as well as ensuring that maintenance work is completed to a high standard.
To create a BOM in SAP PM, you must first identify the components and materials required for maintenance activities on a specific piece of equipment. You can then create a BOM that lists all the required parts and materials, along with their part numbers, quantities, and descriptions. Once the BOM is created, you can use it to plan and schedule maintenance activities, as well as to order parts and materials from suppliers.
BOMs in SAP PM are an important component of the maintenance process, as they provide a detailed breakdown of all the parts required for maintenance activities. They help to ensure that maintenance work is completed efficiently and to a high standard, and they help organizations to optimize their maintenance processes over time by identifying trends in parts usage and maintenance activities.Commonly used T-codes in SAP Plant Maintenance (PM):
1. IW21 - Create Maintenance Order
2. IW22 - Change Maintenance Order
3. IW23 - Display Maintenance Order
4. IW31 - Create Notification
5. IW32 - Change Notification
6. IW33 - Display Notification
7. IP10 - Maintenance Planning Overview
8. IP30 - Scheduling Maintenance Plan
9. IP02 - Change Maintenance Plan
10. IP03 - Display Maintenance Plan
11. IA01 - Create Equipment
12. IA02 - Change Equipment
13. IA03 - Display Equipment
14. IH01 - Functional Location Structure Display
15. IH02 - Change Functional Location
16. IH03 - Display Functional Location
17. IH08 - Equipment Structure Display
18. IH09 - Change Equipment Structure
19. IH10 - Display Equipment Structure
20. IW38 - List of Orders
These T-codes can be used to perform a wide range of tasks in SAP PM, from creating maintenance orders and notifications to managing equipment and functional locations, and more.
SAP Plant Maintenance (PM) provides functionality for measuring and monitoring equipment and maintenance activities. This functionality is used to track key performance indicators (KPIs), identify trends, and optimize maintenance activities over time.
SAP PM for measuring and monitoring key features:
1. Equipment and Maintenance Plan Counters:
SAP PM allows you to define and track equipment and maintenance plan counters. Counters are used to measure and monitor equipment usage and maintenance activities, such as the number of hours a piece of equipment has been in use, or the number of maintenance activities completed.
2. Measurement Documents:
SAP PM allows you to record measurement data and create measurement documents. Measurement documents are used to record data from sensors and other measurement devices, and can be used to track equipment performance over time.
3. Condition Monitoring:
SAP PM provides functionality for condition monitoring of equipment. This includes the ability to define condition-based maintenance plans, create inspection rounds, and record inspection results.
4. KPI Reporting:
SAP PM provides a range of reporting functionality for measuring and monitoring KPIs. This includes the ability to generate reports on equipment usage, maintenance activities, and other key metrics.
5. Integration with Other Systems:
SAP PM can be integrated with other systems, such as Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) and Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES), to provide a comprehensive view of equipment and maintenance activities.
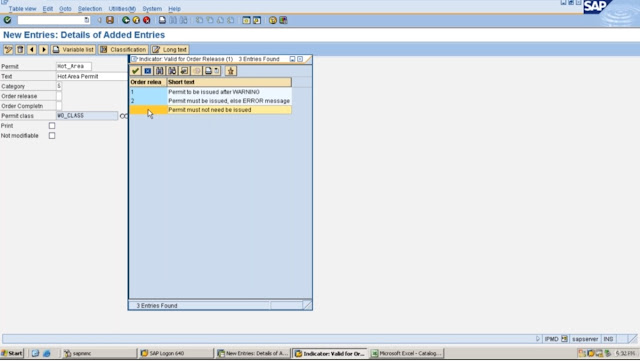
In SAP Plant Maintenance (PM), permits are used to control maintenance work that requires special permissions or safety precautions. Permits are used to ensure that work is performed safely and in compliance with regulatory requirements.
Here are some of the key features and capabilities of SAP PM for managing permits:
1. Permit Types:
SAP PM allows you to define different types of permits, such as hot work permits, confined space permits, and electrical permits. Each permit type has its own set of requirements and safety precautions.
2. Permit Workflow:
SAP PM provides a permit workflow that guides users through the process of creating, approving, and closing permits. This includes the ability to assign roles and responsibilities, set deadlines, and track the status of permits.
3. Permit Creation:
To create a permit, users can use a standard permit template or create a custom permit based on the specific requirements of the work being performed. Users can also attach relevant documents, such as safety data sheets or work instructions, to the permit.
4. Permit Approval:
Once a permit is created, it must be reviewed and approved by authorized personnel before work can begin. SAP PM allows for configurable approval workflows and automated notifications to ensure that permits are approved in a timely manner.
5. Permit Closure:
After the work is completed, the permit must be closed out and signed off by the appropriate personnel. SAP PM allows for the recording of relevant data and the creation of audit trails to ensure that all work is performed safely and in compliance with regulations.
A work permit is a formal written document that is used to authorize and control hazardous or non-routine work activities. Work permits are used to ensure that work is performed safely and in compliance with regulatory requirements and organizational policies and procedures.
Work Permit System Key Features
1. Work Description:
A work permit should include a description of the work to be performed, including the scope, duration, and location of the work.
2. Hazards and Precautions:
The work permit should identify any hazards associated with the work and the precautions that must be taken to ensure the safety of personnel and equipment.
3. Authorization and Responsibility:
The work permit should clearly identify the personnel who are authorized to perform the work and the responsibilities of each individual involved in the work.
4. Control Measures:
The work permit should outline the control measures that will be implemented to manage the hazards associated with the work. This may include the use of personal protective equipment, engineering controls, and administrative controls.
5. Monitoring and Review:
The work permit should include provisions for monitoring and review of the work to ensure that it is being performed safely and in compliance with the permit requirements.
Overall, work permits are an important tool for ensuring that hazardous or non-routine work activities are performed safely and in compliance with regulatory requirements and organizational policies and procedures. By following the guidelines and requirements outlined in a work permit, organizations can minimize the risks associated with these types of work activities and protect the safety and well-being of their personnel and equipment.




Post a Comment